In France, the price of electricity evolves from year to year, especially under the effect of the increase in electricity taxes.These increases may well become commonplace: the Senate has projected an increase in the electricity bill by 50% by 2020.However, energy players keep highlighting the low price of electricity in France compared to its European neighbors ... So, true or false?Overview of the price of electricity in the European Union.
Electricity price for individuals in Europe
Electricity is on average cheaper in France than in its European neighbors, with an average kilowatt hour price of € 0.1765 including tax against € 0.2159 within the European Union for individuals in 2019.However, France is not the cheapest country in Europe for electricity, since it is in the 14th rank of the cheapest countries, on 28 European Union member states.This is explained in particular by the weight of taxes, which represents approximately a third of the price of kWh of electricity in France.
Start by comparing prices among French suppliers!
The selectra comparator allows in a few minutes to classify suppliers from the cheapest to the most expensive and to find the offer that adjust the most to your needs.Electricity comparator
France below the European average
In 2019, the price of electricity in the European Union for individuals established an average of € 0.2,159 including tax/kWh according to Eurostat data.
However, the prize for the cheapest electricity price in Europe is not won by France but by ....Ukraine with 0.0442 € TTC/KWH.If France is only in 25th position out of 39 of the classification of the cheapest countries in Europe (countries excluding EU included), the price of electricity in France is significantly lower than the European average: in 2019, French households paid for their electricity € 0.1765 including tax/kWh on average.In addition, it should be noted that France has gone from 17th to 14th in the European Union (28 countries) in terms of TTC electricity prices for individuals between 2018 and 2019.
So when we make a comparison of electricity prices in Europe, do the French really benefit from a price below their European neighbors?Yes and no...
What is the cheapest European Union country for electricity?The cheapest European Union country for electricity is Bulgaria (0.0997 € including tax/kWh), which is ahead of Lithuania (0.1255 € TTC/KWh) or Hungary (0.1120 € TTC/KWH).
Electricity price for individuals in the European Union in 2019
NOTOT.B.The prices indicated come from the Eurostat database, the European Union Statistical Office.The analysis of electricity prices for households is based on prices for the normalized median consumption tranche of households with an annual electricity consumption between 2,500 and 5,000 kWh.Find more information on average electricity consumption in France and on how to convert your electricity consumption into euros.
Classification of electricity prices in Europe in 2019
What about gas? Regarding the comparison of natural gas prices in Europe, Peco also offer the cheapest prices of the whole European Union.In the trio of the cheapest member states in 2019 are Bulgaria, Lithuania and Hungary.
Electricity prices for other consumers (out-houses) in Europe
France under the European average
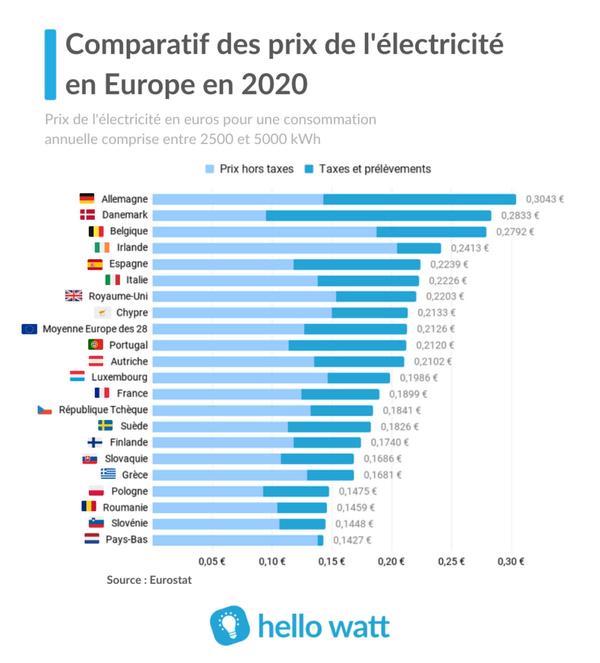
Regarding consumers off-household (professionals, industrialists...), France ranks twenty-fifth from thirty-nine to the rank of the cheapest countries in Europe (countries outside the EU included) for electricity, with a price per kilowatt hour of 0.1024 € HT in 2019.The price of electricity in the European Union for Professionals and Industrialists has established an average of € 0.1251 excl..
For these consumers, the cheapest electricity price of electricity in the European Union is awarded to Denmark, with a price of € 0.0707 excl..
France is located in the thirteenth rank in 2019 of the cheapest countries of the European Union (28 countries), thus losing a place compared to that which it occupied in 2018.As with households, the price of electricity for non-household consumers in France is below the European average.In short, they benefit from rather cheap electricity prices, certainly lower than the European average but which are not among the cheapest countries in Europe.
For this category of consumers, the distinction between new entrants - the countries of central and eastern Europe (PECO) - and the founding member states (Germany, Italy, Luxembourg...) is not relevant.
Electricity prices for consumers out of households in Europe in 2019
NOTOT.B.The prices indicated come from the Eurostat database, the European Union Statistical Office.Analysis of electricity prices for Hors-household consumers is based on prices excluding the average national tax in Euro per kWh for an annual consumption of 500 to 2,000 MWh.
If at European level a consumption between 500 to 2000 MWh is considered "average", it is actually very high for the majority of professionals.It does not represent the classic consumption of small professionals, but rather that of industries and large accounts.
Classification of electricity prices for consumers outside of cleaning in 2019
Why is the price of electricity still relatively cheap in France?
Low production costs: the advantages of nuclear energy
The price of electricity depends, largely, on the cost of the various fuels and the equipment implemented.Each country uses energies in different proportions - this is called the energy bouquet.Very different from one country to another, it is more than 80% dominated by fossil fuels in the world.
In the European Union, France is strongly distinguished from its neighbors by the originality of its energy bouquet.Electricity production in France is indeed dominated by nuclear energy - which represents almost three -quarters of total production.This preponderance of nuclear energy is the result of past strategic choice (development of hydroelectricity and nuclear).These have enabled France to have competitive electricity, not very carved and participated in strengthening the country's energy independence.In all, 19 nuclear power plants and 58 reactors are now installed in France.Note that the share of nuclear in the French electric mix will be brought to 50% by 2025, within the framework of the Energy Transition Act for Green Growth.
Although described, nuclear energy has a major advantage: its production cost guarantees a low electricity price compared to our European neighbors.According to data published by the Energy Regulatory Commission (CRE), the cost of production of nuclear energy is between € 59.8 and € 109 per MWh depending on the age of the power station.
Regarding renewable energies, only hydraulic energy has represented a less significant production cost than that of nuclear: from 15 to 20 €/MWh.This is explained by the fact that the construction costs - colossal - dams have been amortized for a long time.By way of comparison, the earth's wind has represented a cost of € 90/MWh, the offshore wind (less visible) around € 200/MWh and the photovoltaic decreases sharply since it was almost divided by two in five yearsTo go to 142 € per mWh.Finally, the cost of production of thermal energy amounts to 70 or 100 €/MWh depending on the process used (gas, coal, fuel oil).
The share of nuclear in French electricity production contributes to the good results of France concerning greenhouse gas emissions (GHG).The price of nuclear electricity, less sensitive to variations in fossil fuels, also allows better long -term stability.
The comparison of electricity prices between France and Germany
If Germany often acts as a model student in Europe, households across the Rhine pay much higher bills than with us, with a difference of around 75%!And for good reason, the Germans pay at high prices "Energiewende" - or energy transition in French -, implemented from the early 2000s and accelerated following the Fukushima disaster, which gave pride of place to fossil fuelsand renewable.
The German energy model is indeed characterized by a large part of fossil fuels: in 2013, they represented 57.1% of total electricity production against 23.4% for renewable energies and 15.4% for energynuclear (which aims to gradually disappear by 2022).The gradual reduction in nuclear is now offset by renewable energies (16.6% in 2010 against 24.1% in 2013), like wind, biomass or even solar energy.The use of coal (18.5% in 2010 against 19.4% in 2013) and lignite (23% in 2010 against 25.5% in 2015) has particularly exploded… by the same GHG emissions by the same.
In addition, electricity taxes are much higher across the Rhine, in particular due to contributions for the financing of renewable energies.An "ecological" tax thus targets German households to moderate their electricity consumption.It is that the German government has chosen to bring most of the effort linked to the energy transition to individuals, with a view to maintaining the competitiveness of companies.
Evolution of the price of electricity in Europe
The increase in the price of electricity in France is part of a European context of increase in the price of electricity, under the effect of the introduction of green energies, the increase in nuclear energy costs,the increase in the cost of petroleum and gas products.In 2019, according to Eurostat, the price of French KWH was generally located in the European average (average of the 28 countries of the European Union), with a level lower than the countries of Western Europe.









SOS Public Hospital: our revelation...
The best smartphones for gaming in...
Google Maps: activate the new widge...
Free tips in video: Free Mobile off...